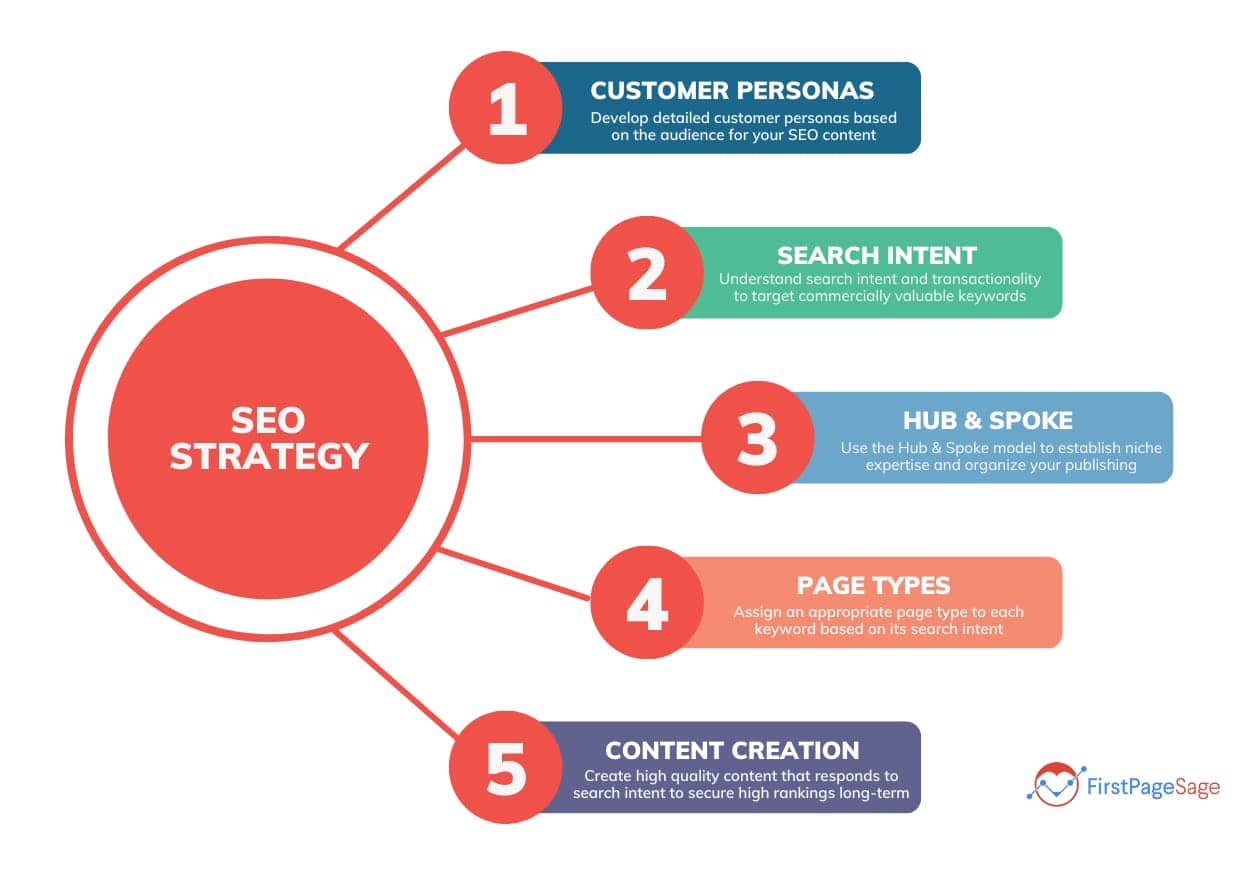
No one knows exactly how search engine algorithms work—especially Google’s.
Which is why there are so many SEO myths. From made-up keyword types to claims backed by misinterpreted data.
We’re about to go over some of the main SEO myths right now. So you don’t waste time chasing incorrect tips.
1. There’s an Ideal Keyword Density
The ratio of a term’s occurrences on a webpage to the total number of words on that page is known as keyword density. It can be computed with the following formula:
The ratio of the target term’s occurrences in the content to the total words in the content is known as the keyword density.
In a 1,000-word document, the keyword density would be 2% if the term “keyword density” was used 20 times.
Optimal keyword densities are regularly recommended by SEO specialists. According to some, 2% to 3% is ideal. Some suggest that you should aim for 4% to 5%.
However, there isn’t a perfect keyword density.
Google has stated this several times. notably in a 2011 film about keyword density.
Rather than calculating the number of times you bring up a target
Then, enter your article text and target keywords into the spaces provided.
The tool will then tell you if you’ve used your target keyword too many times.
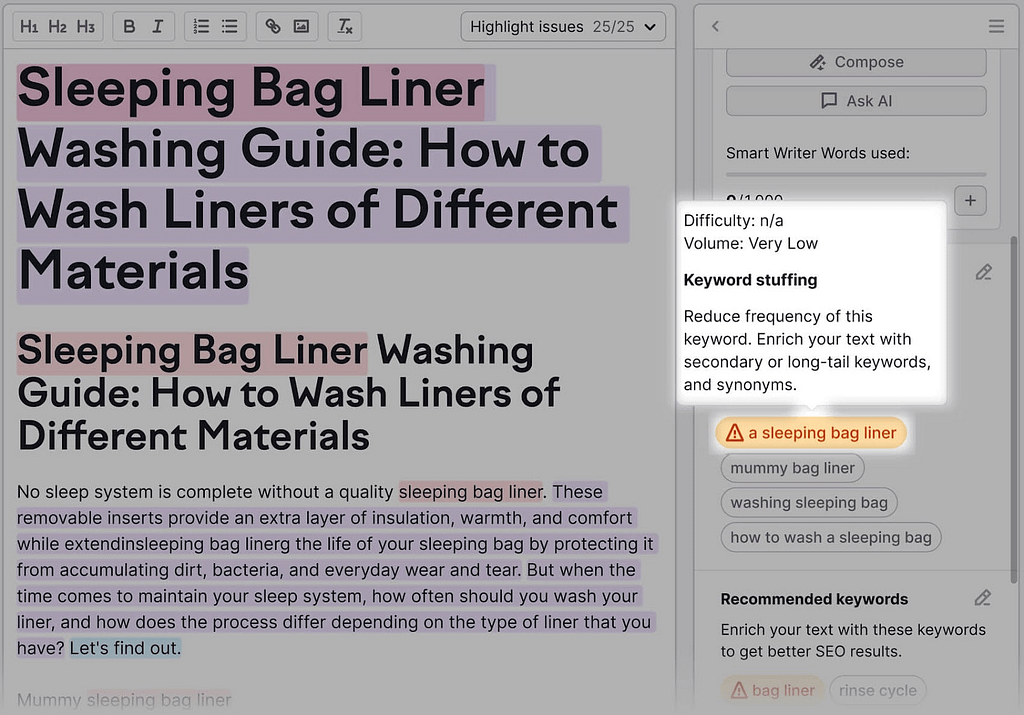
Simply remove the keyword mention or rephrase. So your content doesn’t go overboard with keyword use.
2. LSI Keywords Boost Search Rankings
Many search engine optimisation specialists assert that Google understands and ranks material using latent semantic indexing (LSI), a retrieval technique that assesses the associations between words within a collection of pages.
Words or phrases that are related to your target keywords are considered LSI keywords. aren’t synonymous, though.
For instance, some would claim that “credit limit” and “accounts opened” are LSI keywords for “credit score.” but not the synonym “credit rating.”
However, Google is concerned with search intent and semantics.
Google wants you to create in-depth, really helpful material. Additionally, when you write a lot on a subject, you automatically incorporate semantic keywords into your writing.
3. You Should Only Target High-Volume Keywords
High-volume keywords are keywords that get thousands to millions of searches per month. And they’re typically shorter search terms.
For example, “SEO” is a high-volume keyword.
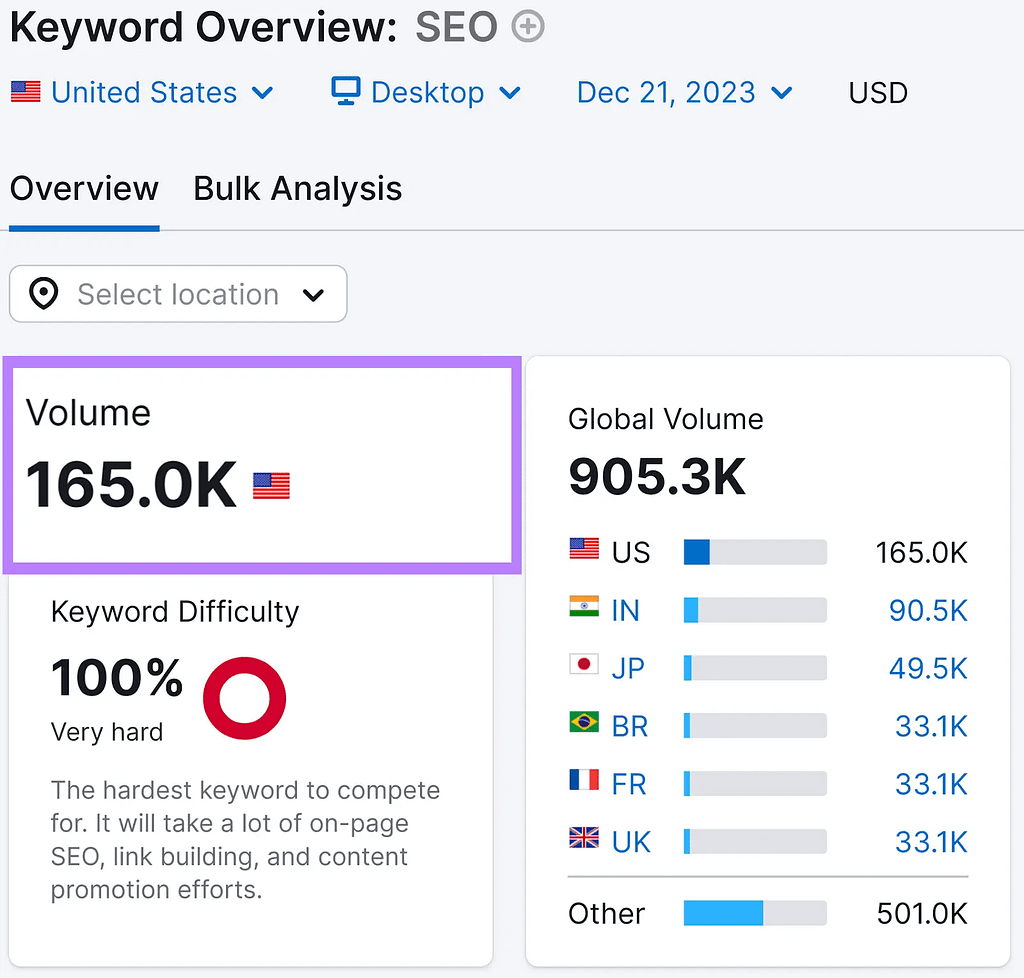
Some so-called SEO specialists assert that you should prioritise high-volume keywords over low-volume ones at all times. due to the latter’s low traffic generation.
However, big volume keywords are typically very competitive as well. and frequently not very niche-specific.
Conversely, low-volume keywords typically face less competition. and are frequently more tailored to your business.
Assume you manage a website where users may search for the cheapest airfares.
Approximately 2.2 million searches for the popular keyword “cheap flights” are made each month.
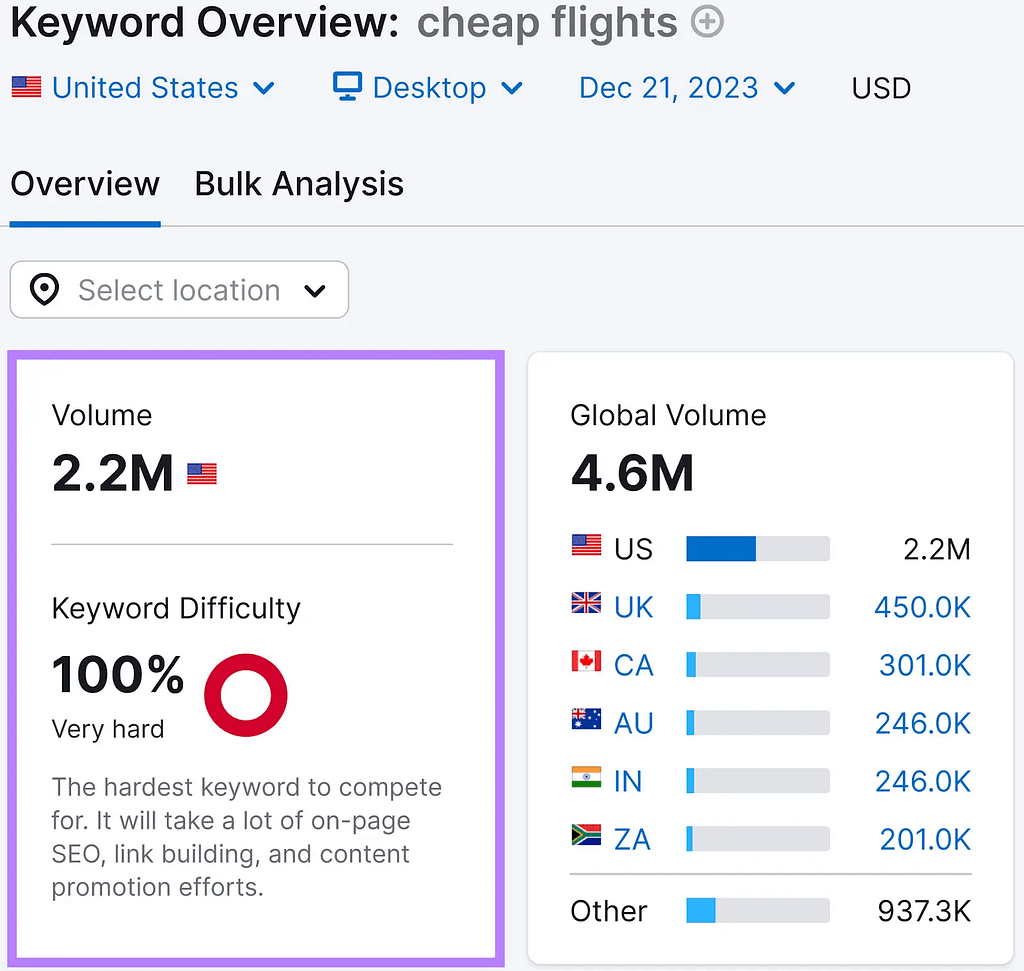
It will be challenging to outrank Cheapflights, Kayak, and Skyscanner, the websites that rank highest among the search results for “cheap flights.”
Observe the search purpose as well—the rationale behind a search. It’s evident from perusing the search results that people are looking to get inexpensive airline tickets. not reading an educational manual of any kind.
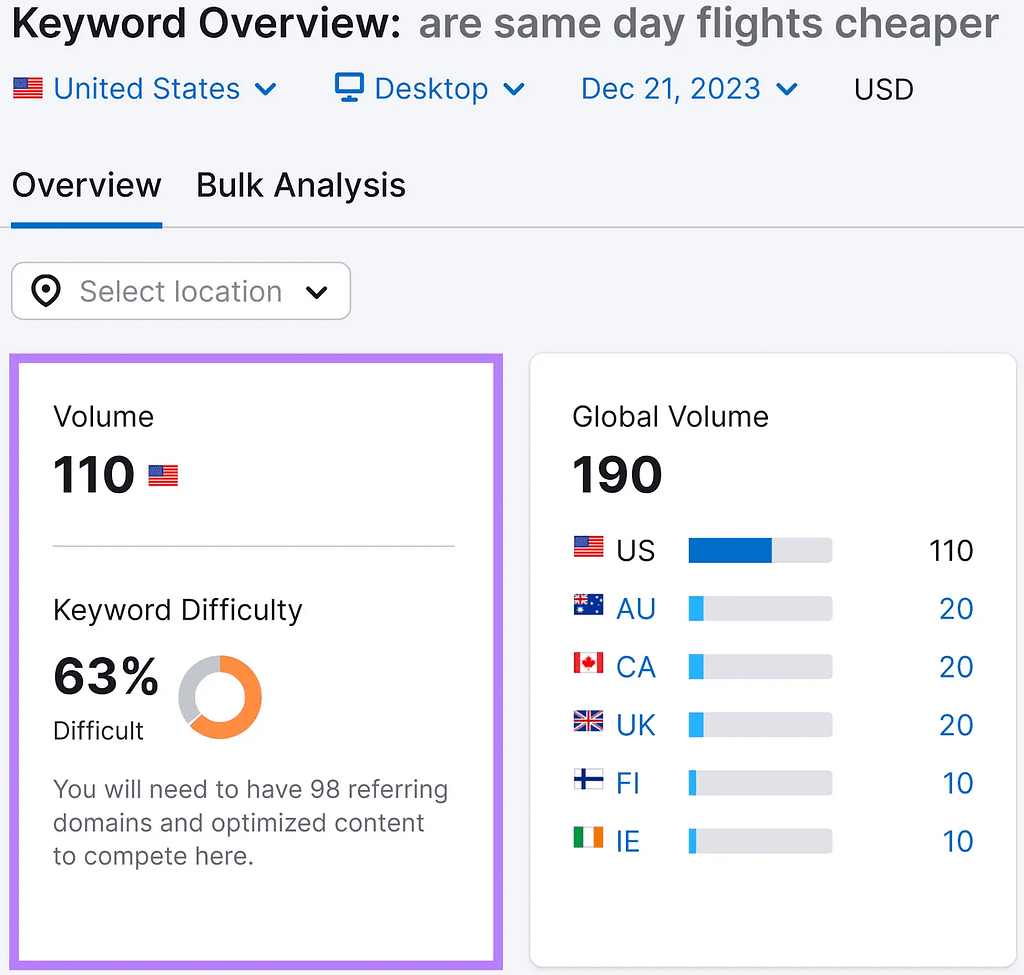
Instead, let’s examine a pertinent low-volume keyword.
There are only about 110 searches each month for “are same day flights cheaper.”
4. Domain Authority Is a Ranking Factor
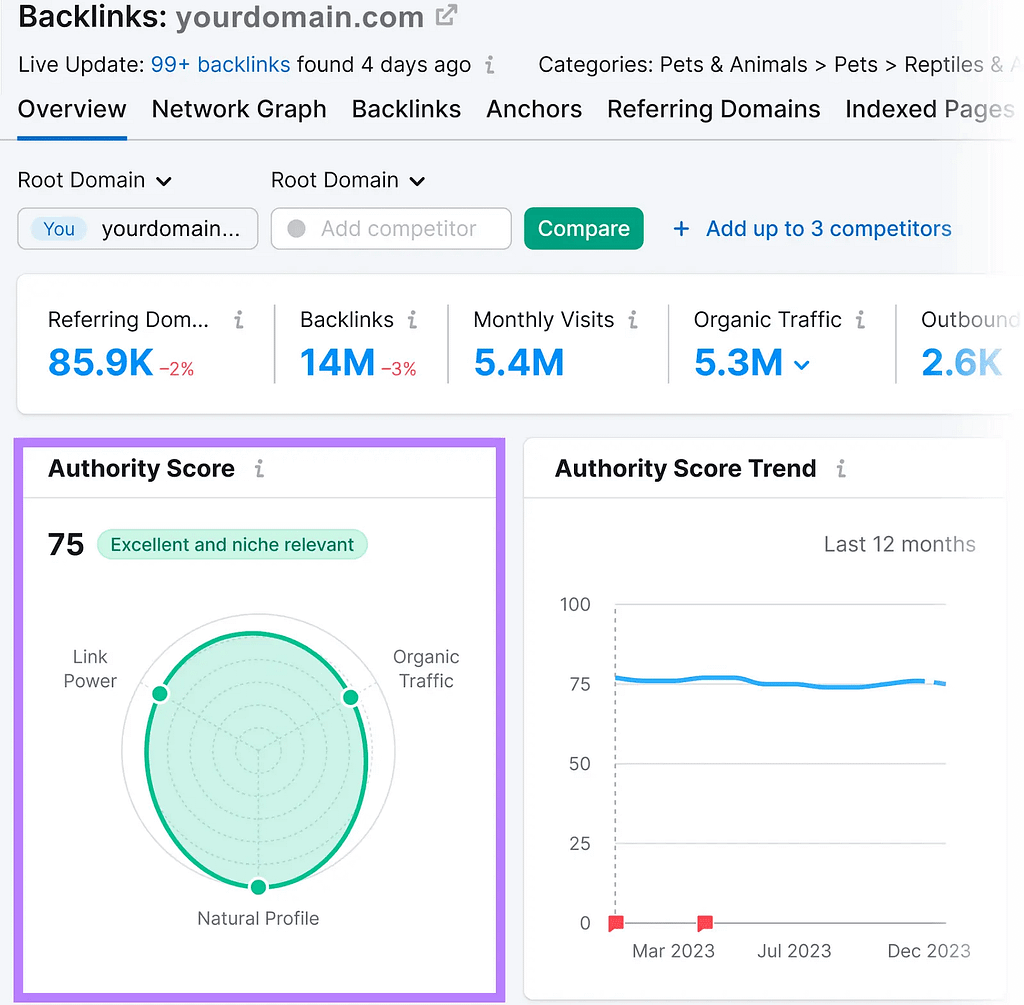
Domain authority indicates how strong and trustworthy a website is.
But as opposed to what some SEO experts claim, it isn’t a ranking factor. And has no direct impact on rankings.
Depending on the particular measure. Additionally, verified ranking variables are used to determine LINKSUBMIISSIONFUNDA Authority Score:
The amount and calibre of backlinks
The anticipated monthly volume of organic traffic
Any signs of spam that suggest a ranking manipulation attempt
Therefore, Authority Score can inform you how well a specific website holds up in comparison to similar websites, even though it isn’t a ranking criteria. Additionally, you can use the LINKSUBMISSIONFUNDA Domain Overview tool to verify it for any website.
Just launch the application and enter the URL of the website you wish to examine. then select “Search.”
Tool for Domain Overview
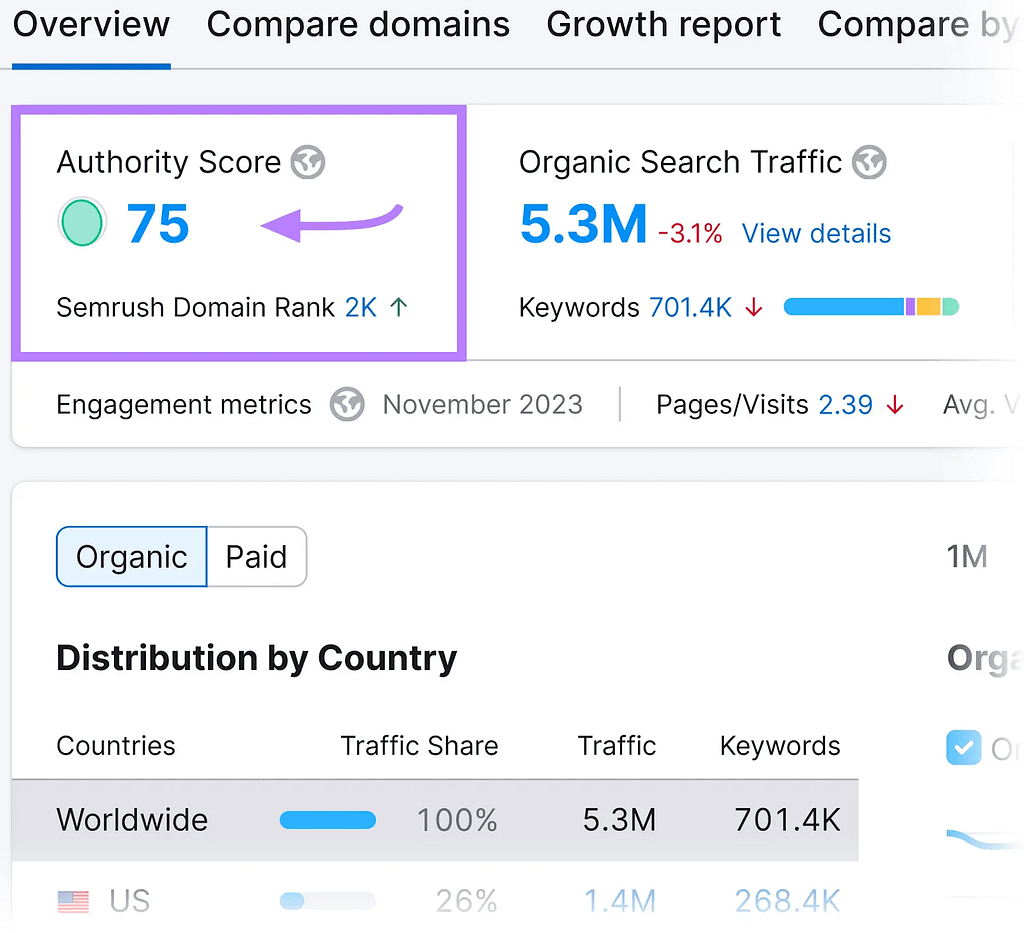
The Authority Score is displayed at the top of the report.
“Authority Score” widget in Domain Overview dashboard with “75” highlighted
Clicking the number will lead you to a Backlink Analytics report.
It will display the distribution of the Authority Score among the three major
Just launch the application and enter the URL of the website you wish to examine. then select “Search.”
You’ll see the Authority Score at the top of the report.
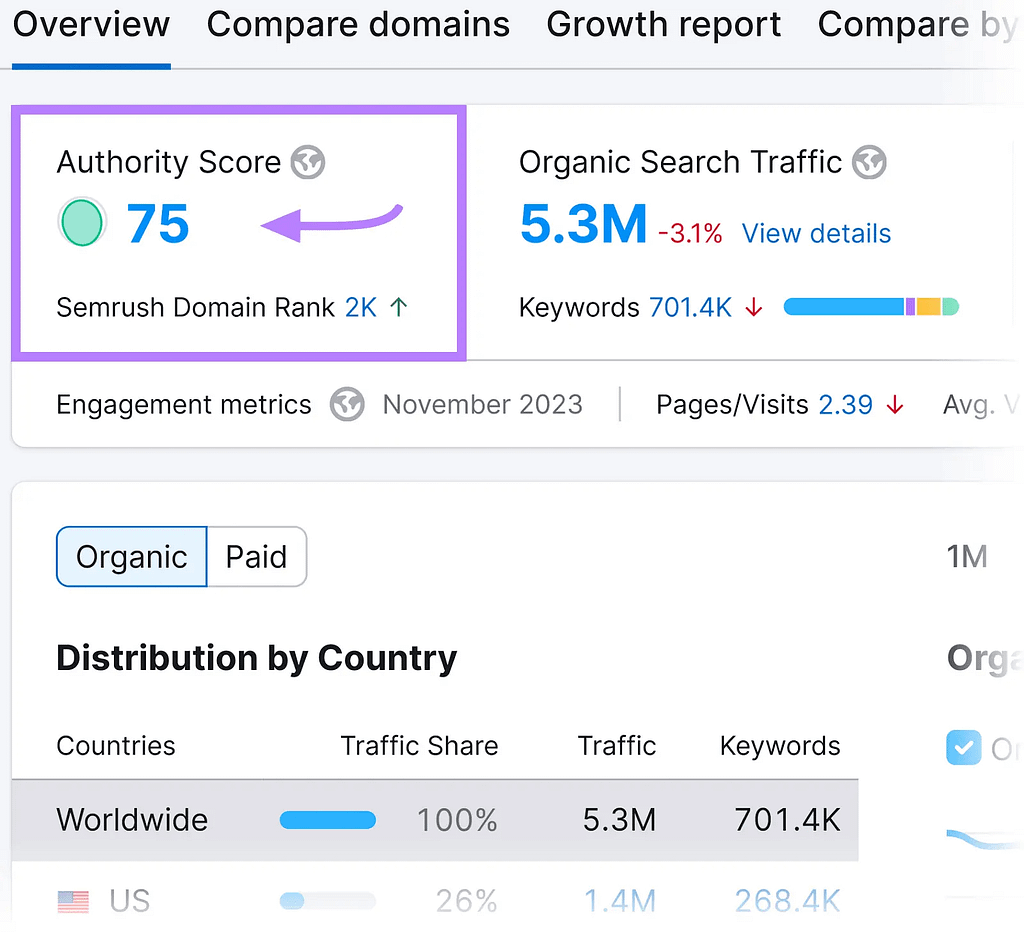
Clicking the number will lead you to a Backlink Analytics report.
It will display the distribution of the Authority Score among the three crucial elements:
5. Google Always Penalizes Duplicate Content
Any content that is a page that is almost identical to another page or exactly the same as another is considered duplicate content. That could refer to several pages on several websites or several pages on one website.
This is an illustration of what can be seen as redundant content:
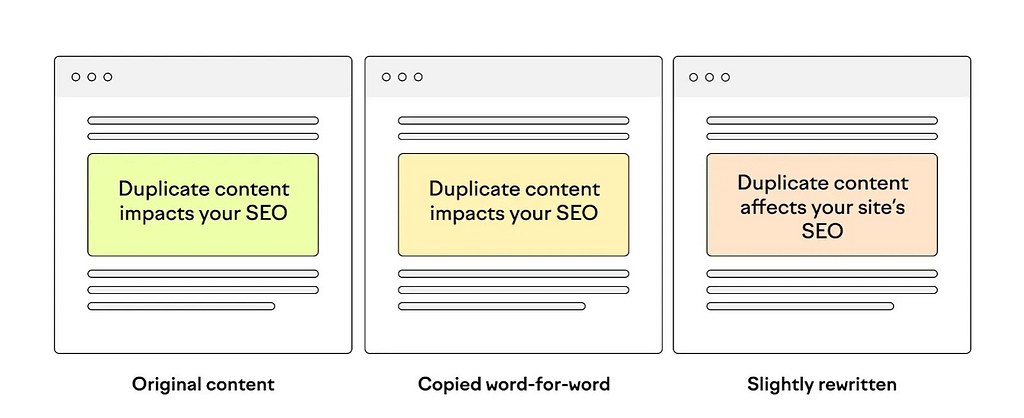
Google has said clearly that it does not penalise duplicate material, contrary to what many SEO experts and content authors believe—as long as the duplication isn’t done with the intention of misleading search engines.
When duplicate material appears on your own website, Google may not be able to determine which of the results is the “main” one and should appear in search results, which can negatively impact your SEO performance. It may cause those pages to rank lower or not at all.
Therefore, avoiding duplicating content as much as possible is still a smart idea.
Use Semrush’s Site Audit to quickly identify duplicate pages on your website.
Just type your domain name into the designated field. Next, select “Start Audit.”
6. Long-Form Content Always Performs Better
Some SEO experts claim that long-form content performs better on Google.
After all, our 2023 State of Content Marketing Report indicates that publications longer than 1,100 words typically rank higher in organic search results.

But it’s an SEO myth that longer articles rank better due to their length.
A 2,000-word article that covers all the wrong subtopics probably won’t rank. But a 1,000-word article that exhaustively covers a certain topic likely will.
In other words, covering the topic comprehensively and in a way that matches search intent is what helps content rank well. Not word count.
7. More Content Is Always Better
The frequency of publication and the effectiveness of the material are inextricably linked.
According to our 2023 State of Content Marketing Report, about 25% of successful blogs post content each day. Furthermore, underperforming ones typically publish fewer times.
However, this does not imply that publication itself always produces better outcomes.
Moreover, Google Search Central presented a webinar to debunk this SEO fallacy. and made it clear that creating content for its own sake is not something you should do.
Meeting the needs and desires of your audience should be the main goal of your content strategy instead.
8. Meta Description Is a Ranking Factor
A meta description is a little bit of code that sums up the information on your website.
Search engine optimisation does not directly use meta descriptions as a ranking component (SEO). In order to establish ranks, search engines like Google largely use algorithms that examine web page content, relevancy, backlink quality, and other variables.
Though they might not have a direct effect on rankings, meta descriptions are very important for getting clicks from search engine results pages (SERPs). The click-through rate (CTR) can be raised by persuading readers to click on your link using a compelling meta description. A greater CTR may imply to search engines that your material is interesting and relevant, which could eventually result in higher ranks.
Making accurate and captivating meta descriptions that appropriately convey the page’s content is crucial. Despite not being a direct determinant of ranking, they do.
8.SEO Is Something You Do Once
There’s a lot of preliminary work you have to do for your SEO efforts to pay off.
So, is SEO a one-time thing you’re done with once you’ve achieved solid rankings?
Not at all.
You need to regularly monitor performance and keep your content updated. To ensure that your site continues to appear in search engine results.
There are a few things you can do to keep your website performing well.
Instead of being a one-time event, search engine optimisation, or SEO, is a continuous activity. The digital environment is dynamic and ever-changing, encompassing user behaviours, search engine algorithms, and competition. Here are some explanations for why SEO is a continuous process:
Algorithm Updates: In order to give users more useful and relevant results, search engines update their algorithms on a frequent basis. Website rankings may be impacted by these modifications. It is necessary that you adjust to these algorithm changes if you want to keep or increase your presence in search results.
Competitive Environment: It’s possible that your rivals are using SEO as well. You might need to modify your tactics as they make modifications to their websites and content in order to remain competitive.
Updates to the material: Relevant and up-to-date content is essential for SEO. Frequently updating